Perticle distribution of "Maglux ST"
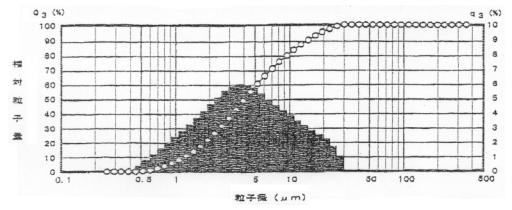
Particle diameter in micron
Technical Information
1. Types of Maglux
2. Technical information of Maglux
2-1. Chemical Composition
2-2. Dehydration
2-3. Shape and Dispersion in plastics
3. Special Properties in Plastic Compound
3-1. Polypropylene
3-2. Polyethylene
3-3. Ethylene Ethyl Acrylate
3-4. Ethylene-vinyl Acetate
3-5. Ethylene-propylene Rubber
Remarks: This technical information is based on the actual experimental value for the customer's reference and not guaranteed performance of "Maglux".
1.The Type of Maglux
"Maglux" is micronized and surface treated natural mineral "Brucite", that contains mainly Magnesium Hydroxide. For the customers various requirements and for the type of plastics, some type of surfactant is available.
|
Type |
Surfactant |
|
Maglux ST |
Stearic Acid 1%,2%,3% |
2.Technical information
2-1. Characteristic of Maglux
|
Chemical Composition(%) |
MgO |
CaO |
Fe2O3 |
Acid insolvement |
Free water |
|
65.4 |
0.69 |
0.35 |
1.37 |
0.26 |
|
|
Whiteness(WB) |
84.7 |
||||
|
Average particle diameter (D50) |
4.04 micron |
||||
|
Area/weight ratio (BET) |
6.3m2/g |
||||
|
Sieve test |
+45 micron max.0.05% |
||||
|
True spec. density |
2.4 |
||||
|
Bulk density |
0.3 |
||||
The value of table is acutual experimental value of "Maglux ST"
There are not much differencies in the physical properties is observed between gMaglux STh and other types (gMaglux NAh,hMaglux CAh, hMaglux MKh)
Perticle distribution of "Maglux ST"

Particle diameter in micron
2-2. Dehydration
"Maglux" has nearly the same dehydraion-characteristic (dehydration temperature, the rate of dehydration and endotherm value) of the commercial magnesium hydroxide from sea-water.
TG/DTA diagram
Maglux (A) and commercial magnesium hydroxide from sea-water
(F)
2-3. Shape and Dispersion in plastics
SEM (scanning electron microscope)
3-1 Polypropylene
Low-Density polyethylene (LDPE)
Block-type melting point:163deg. Density:0.9
MFR[230deg. 2.16kgf]:0.7
Composition:PP(100),Flame Retardants(120),Calcium Stearate(1)
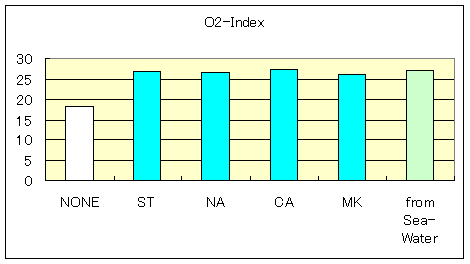
Characteristic of Polypropylene-Compound
| Fire Retardants | Maglux | Magnesium Hydroxide | ||||
| Surfactant | Without Fire Retardant |
ST | NA | CA | MK | from Sea-Water |
| O2-Index | 18.3 | 26.9 | 26.7 | 27.4 | 26.2 | 27.0 |
| MFR(230deg. 2.16Kgf) | 0.79 | 0.92 | 0.86 | 0.92 | 0.79 | 1.13 |
| Yield Strength(kgf/cm2) | 231 | 153 | 162 | 150 | 165 | 146 |
| Tensile Strength(kgf/cm2) | 235 | 153 | 163 | 150 | 165 | 146 |
| Maximal Elongation(%) | 10 | 3 | 6 | 3 | 6 | 5 |
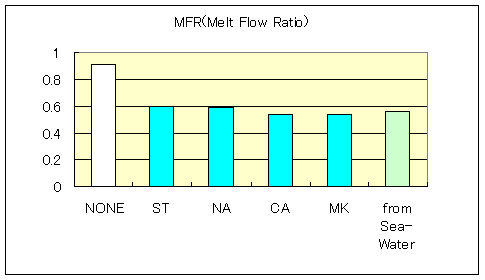
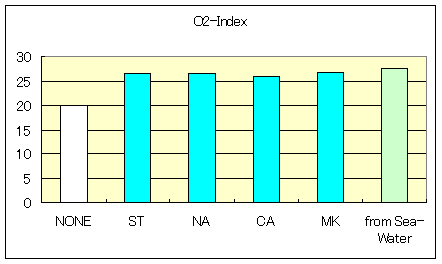
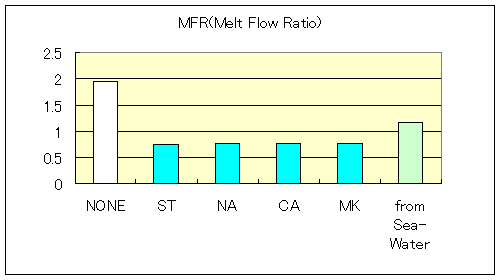
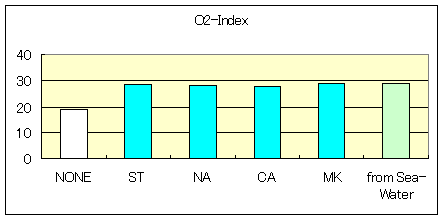
3-2. Polyethylene (PE)
Straight-chain type (LDPE)
Melting point:122deg Density:0.924 MFR[190deg
2.16kgf]:0.85
Compounding:PE(100), Flame retardants(120),
Calcium Stearate@C(1)
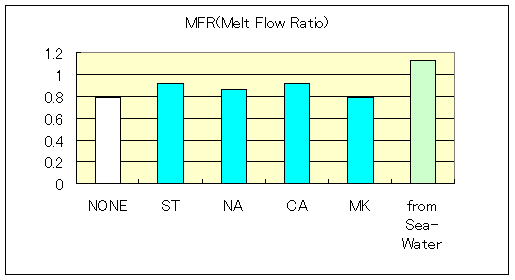
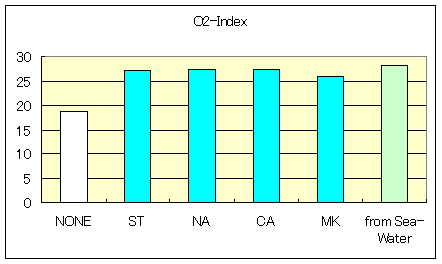
Characteristic of Low dencity Polyethylene-Compound
| Fire Retadants | Maglux | Magnesium Hydroxide | ||||
| Without fire retardant |
ST | NA | CA | MK | from Sea-Water | |
| O2-Index | 18.7 | 27.2 | 27.4 | 27.4 | 26.0 | 28.2 |
| MFR(190deg 2.16Kgf) | 0.91 | 0.6 | 0.59 | 0.54 | 0.54 | 0.56 |
| Yield Strength(kgf/cm2) | 107 | 102 | 100 | 107 | 99 | 117 |
| Tensile Strength (kgf/cm2) | >172 | 102 | 100 | 107 | 99 | 117 |
| Maximal Elongation(%) | >620 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 9 |
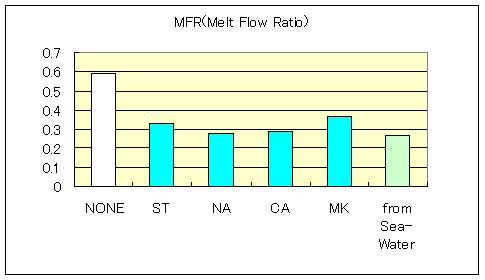
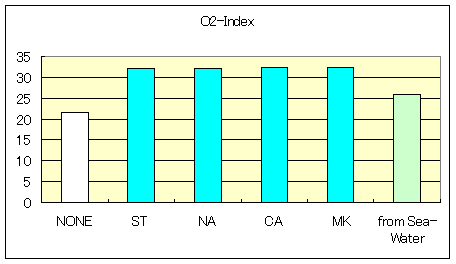
3-3. Ethylene Ethyl Acrylate (EEA)
Ratio of co-monomer:15% Melting point:100deg.
MFR[190deg. 2.16kgf]:0.75
CompoundingFEEA(100), Flame retardants(120),
Calcium stearate(1)
Characteristic of Ethylene Ethyl Acrylate Compound
| Fire Retadants | Maglux | Magnesium Hydroxide | ||||
| Surfactant | Without Fire retardant |
ST | NA | CA | MK | from Sea-Water |
| O2-Index | 20 | 26.5 | 26.5 | 25.9 | 26.7 | 27.5 |
| MFR(190deg. 2.16Kgf) | 0.59 | 0.33 | 0.28 | 0.29 | 0.37 | 0.27 |
| Yield Strength(kgf/cm2) | 36 | 55 | 57 | 59 | 49 | 55 |
| Tensile Strength (kgf/cm2) | >110 | 92 | 90 | 85 | 72 | >92 |
| Maximal Elongation(%) | >520 | 590 | 580 | 570 | 515 | >600 |
3-4. Ethylene-vinyl Acetate (EVA)
Ratio of co-monomer:15% Melting pointF88deg. MFR[230deg. 2.16kgf]:2.0
Compounding: EVA(100), Flame retardants(120),
Calcium stearate(1)
Characteristic of Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate Compound
| Fire Retadants | Maglux | Magnesium Hydroxide | ||||
| Surfactant | without fire retardant |
ST | NA | CA | MK | from Sea-Water |
| O2-Index | 21.6 | 32.2 | 32.2 | 32.4 | 32.4 | 26.0 |
| MFR(190deg. 2.16Kgf) | 1.95 | 0.73 | 0.75 | 0.76 | 0.75 | 1.18 |
| Yield Strength(kgf/cm2) | 46 | 68 | 82 | 96 | 75 | 68 |
| Tensile Strength (kgf/cm2) | >121 | 76 | 82 | 96 | 75 | 73 |
| Maximal Elongation(%) | >540 | 18 | 21 | 29 | 24 | 24 |
3-5. Ethylene-propylene Rubber (EPR)
Composition: Ethylene 61wt%, Propylene 33wt%,
END 6wt%
Compounding: EPR(100), Flame retardants(120), Calcium stearate(1),
Stearic acid(1), Sulfur(1.5), Zinc oxide(5),
TMTM(1.5), MBT(0.5)
Vulcanization:160deg. 30min.
Characteristic of Ethylene-Propylene Rubber
Compound
| Fire Retadants | Maglux | Magnesium Hydroxide | ||||
| Surfactant | Without fire retardant |
ST | NA | CA | MK | from Sea-Water |
| O2-Index | 18.8 | 28.7 | 28.2 | 27.8 | 28.8 | 29.1 |
| Yield Strength(kgf/cm2) | 3 | 13 | 14 | 14 | 13 | 12 |
| Tensile Strength (kgf/cm2) | 19 | >42 | >44 | >44 | >43 | 36 |
| Maximal Elongation(%) | 270 | >450 | >460 | >460 | >440 | 420 |
(Remarks)
Supplemental remarks to technical information about gMAGLUXh
1. gTechnical informationh is based on the actual experiment. Each plastic resin is selected from a standard series, which can be widely found in the market. At first each resin was mixed with a flame retardant, a lubricant, which we use Calcium Stearate , and so on. A 2-roll machine was used for the mixing operation and a specimen with 2mm thickness was prepared.
2. The purpose of this experiment is finding out a difference between MAGLUX and a famous flame retardant from sea-water.
3. The surfactant loadings is 1%wt by MK-Type and by other types is 2%wt.
4.. The comparison MAGLUX vs. Flame retardant from sea-water, according
to our experiments.
Now we supply only ST type, with stearic acid surface treated..
In short:
(1). O2-Index is MAGLUX is better or nearly same to the competitor.
(2). Strength is MAGLUX is better or nearly same to the competitor.
(3). MFR-value is the competitor is better or nearly same to MAGLUX.
Reasons:
Perhaps the diameter and form of particle may cause this result. MAGLUX has a diameter of 3-4 micron and BET-value of 6-8 m2/g, whereas the Competitor has a diameter of 1-2 micron and BET-value of 4-7m2/g. It means, the shape of MAGLUX far from sphere as the competitorfs, which the photo of SEM (scanning micro scope) shows. This aspheric surface gives a toughness to the materials but removes a flow properties.
Further information:
5. MAGLUX ST (with Stearic Acid surface treated)
For the application to the various compound,
the ratio of stearic acid by MAGLUX ST can be varied from 1% to 3%.
6. The problem of percentage of free water.
Conventionally a percentage of free water by MAGLUX ST is under 0.5%, which is higher than flame retardant from sea-water, because the synthetic chemically produced flame retardant has a drying process at the end of its fabrication.
Although MAGLUX is packed in the 3-layer with 1-layer laminated craft paper bag, CA-type and NA-type get slowly moisture in the long time, especially if they are stored in the relative higher humidity.
Some of our users settle a dryer before kneading, even the ST-Type, which has good hydrophobic property.
7. Coloring
Although MAGLUX has a good whiteness, it can get easy colors by some additives, for example anti-oxidizing agent.
8. The development of white flecks
Chemically, magnesium hydroxide reacts with CO2-gas and water-content in the normal atmosphere. At the result white flecks can be found.
This tendency is by magnesium hydroxide from sea-water is stronger.
9. Result
There are clearly differences between MAGLUX and flame retardant from sea-water. That is why the compounding makers can not change a flame retardant from sea-water synthesized to MAGLUX without changing the blending methods. Only plastic goods manufacture, who has developed an original blending Know-How for MAGLUX, can use this flame retardant.
To make a compound by blending and kneading is very sophisticated process and its variations are existing fast infinitely. For each manufactures Know-How of this process is one of the confidential matters.
Therefore, the development the Know-How at
the user-side must not be omitted by any
means.
written by H.Komatsu,
E-Mail: komatsu-h@shinko-kogyo.co.jp